- SwiftUIプロジェクトの新規作成
- VStackとHStackとZStack
- Xcodeで定義されている要素の内容や説明をみる
- VStackのサンプルコード
- HStackのサンプルコード
- ZStackのサンプルコード
- SwiftUIでのprint関数の使い方
- SwiftUI内でのfor文の使い方
- SwiftUI内でのForEach文の使い方
- SwiftUIのボタンタップでテキストを変更する
- SwiftUIのリストの基本形
- SwiftUIのリストにセクションを追加
- SwiftUIのリストにナビバーを追加
- SwiftUIでナビゲーションによる画面遷移
- SwiftUIのモーダルビュー
- SwiftUIのモーダルフルスクリーン
- SwiftUIでナビバーを非表示にして、戻る。
- NavigationStackとよる画面遷移
- ButtonによるViewの入れ替え
- SwiftUIのCharts(iOS16〜)
- SwiftUIのChartsのBarMarkの積層(iOS16〜)
- SwiftUIのChartsのBarMarkの並列(iOS16〜)
- SwiftUIのテキストフィールド付きのAlert
- SwiftUIのPickerの横向き
- UIKit内でSwiftUIを表示する
- SwiftUIでの図形表示
- SwiftUIでつまんで動かす
- SwiftUIでの時間付きアニメーション
- SwiftUIのToggleによるアニメーション
- SwiftUIのボタンのアニメーション
- SwiftUIにおけるボタンエフェクト
- SwiftUIの.timingCurve
- SwiftUIのアニメーションの演習
- RealityKitとSwiftUIで、球体とボックスと平面を表示する。
- RealityKitとSwiftUIで、文字オブジェクトを表示する。
- RealityKitとSwiftUIで、usdzファイルを表示する。端末基準。
- RealityKitとSwiftUIで、usdzファイルを表示する。平面基準。
- RealityKitとSwiftUIで、3つのusdzファイルを表示する。平面基準。
SwiftUIプロジェクトの新規作成
1。Xcodeを起動する。
2。「Create New Project」をクリック。
3。上のタブのiOSを選択する。(iOSアプリを作成すれば、ipad、mac、VisionProでも配信できる)
3。「App」を選択し、「next」をクリック。
4。プロジェクトの項目を入力する。
- Product Name:プロジェクト名。(自分がわかりやすいもの)
- Team:開発者登録をしていないのであれば「None」のまま。登録していればApple IDの名前。
- Organization Identifier:開発者(組織)の識別子。他と被らないように、自分のwebサイトアドレスを逆転したものが推奨されている。(例:com.xxxxxxxx)
- Bundle Identifier:上の情報から自動生成される。後で変更することができる。アプリを配信する場合は、この識別子に対して配布証明書を作成する。
- Interface:「SwiftUI」を選択。
- Language:「Swift」
- Strage:「None」
- Host in CloudKit:初期設定のまま「チェックなし」
- Include Tests:後から追加できるので「チェックなし」。テストファイルを作成するかどうか。
- 「Next」をクリック。
- Create Git repository on my Mac:「チェックなし」。リポジトリとは、ファイルやディレクトリの状態を記録する場所のこと。gitを使用しないのであれば、チェックを外す。
- ファイルを保存先を選択し、「Create」をクリック。
5。Xcodeのプロジェクトが起動される。左上の再生ボタンで、シュミレーター上で動作させてみる。
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
VStack {
Image(systemName: "globe")
.imageScale(.large)
.foregroundStyle(.tint)
Text("Hello, world!")
}
.padding()
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}VStackとHStackとZStack
1。レイアウトコードは基本的に「var body: some View」の中に書いていく。
2。VStack:縦方向(Vertical:垂直、Stack:積み重ね)
3。HStack:横方向(Horizon:水平)
4。ZStack:奥行き(Z:Z軸)
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
//縦方向、上から下へ。
VStack {
Text("縦その1")
Text("縦その2")
}
//横方向、左から右へ。
HStack {
Text("横その1")
Text("横その2")
}
//奥行き方向、奥から手前へ。
ZStack {
Text("奥行きその1")
Text("奥行きその2")
}
}
}
//右サイドのプレビューを実施している。
#Preview {
ContentView()
}Xcodeで定義されている要素の内容や説明をみる
「VStack」のコード上で、option + クリックすると、要素の説明と簡単なサンプルが表示される。
「VStack」のコード上で、command + クリックすると、要素を宣言しているコードが表示される。
VStackのサンプルコード
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
VStack(alignment: .trailing, spacing: 10)
{
ForEach(1...10, id: \.self)
{
Text("Item \($0)")
}
}
}
}
//右サイドのプレビューを実施している。
#Preview {
ContentView()
}| alignment(並べること) (デフォルトは.center) | |
| .leading | 左合わせ |
| .center | センター合わせ |
| .trailing | 右合わせ |
| spacing(CGFloat) (デフォルトはnull) | |
| 要素と要素の間の余白 | |
| マイナスにすると順番が逆になる | |
HStackのサンプルコード
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
HStack(alignment: .top, spacing: 10
) {
ForEach(1...5, id: \.self) {
Text("Item \($0)")
}
}
}
}
//右サイドのプレビューを実施している。
#Preview {
ContentView()
}| alignment(並べること) (デフォルトは.center) | |
| .top | 上合わせ |
| .center | センター合わせ |
| .bottom | 下合わせ |
| .firstTextBaseline | 最初の文字のベースラインを合わせる |
| .lastTextBaseline | 最後の文字のベースラインを合わせる |
| spacing(CGFloat) (デフォルトはnull) | |
| 要素と要素の間の余白 | |
| マイナスにすると順番が逆になる | |
ZStackのサンプルコード
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
let colors: [Color] = [.red, .orange, .yellow, .green, .blue, .purple]
var body: some View {
ZStack {
ForEach(0..<colors.count) {
Rectangle()
.fill(colors[$0])
.frame(width: 100, height: 100)
.offset(x: CGFloat($0) * 10.0,
y: CGFloat($0) * 10.0)
}
}
}
}
//右サイドのプレビューを実施している。
#Preview {
ContentView()
}SwiftUIでのprint関数の使い方
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
VStack {
}
.onAppear{
//onAppear内であれば、print関数が使用できる。
print("東京")
//東京
}
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}
SwiftUI内でのfor文の使い方
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
VStack {
}
.onAppear{
//onAppear内であれば、print関数が使用できる。
let stringArray:[String] = ["東京", "大阪", "福岡"]
for number in stringArray.indices {
print(stringArray[number])
}
//東京
//大阪
//福岡
}
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}
SwiftUI内でのForEach文の使い方
ForEach文で要素を繰り返し作成することができる。
「Non-constant range: not an integer range」のアラートが出たら、「, id: \.self」を追加する。
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
let stringArray:[String] = ["東京", "大阪", "福岡","沖縄"]
var body: some View {
//VStack内は「@ViewBuilder」という、ビューを構築する部分なので、for文は使用できない。
VStack {
ForEach(stringArray.indices, id: \.self) {
Text(stringArray[$0])
}
}
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
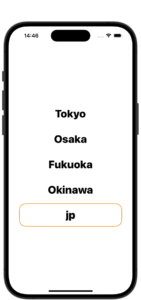
}SwiftUIのボタンタップでテキストを変更する
import SwiftUI
var MainStringArray:[String] = ["東京", "大阪", "福岡","沖縄"]
struct ContentView: View {
@State var bottomTap = false
@State var buttonTitle = "en"
@State var buttonBackGroundColor:Color = .mint
@State var stringArray = MainStringArray
var body: some View {
VStack {
//テキスト群
ForEach(stringArray.indices, id: \.self) {
Text(stringArray[$0])
}
.padding()
//ボタン、枠線付き。
Button(action: {
buttonAction()
}) {
Text(buttonTitle)
.accentColor(Color.primary)
//.background(buttonBackGroundColor)
.padding()
.frame(width: UIScreen.main.bounds.size.width - 100, height: 40)
.shadow(color: .gray, radius: 1, x: 0, y: 0)
}
.padding()
//.background(buttonBackGroundColor)
.cornerRadius(20)
.overlay(
RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 20)
.stroke(buttonBackGroundColor, lineWidth: 2)
)
}
}
//ボタンアクション
private func buttonAction(){
if bottomTap == false {
bottomTap = true
buttonTitle = "jp"
MainStringArray = ["Tokyo", "Osaka", "Fukuoka","Okinawa"]
stringArray = MainStringArray
buttonBackGroundColor = .orange
} else {
bottomTap = false
buttonTitle = "en"
MainStringArray = ["東京", "大阪", "福岡","沖縄"]
stringArray = MainStringArray
buttonBackGroundColor = .mint
}
print(stringArray)
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}
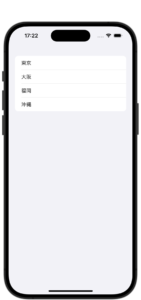
SwiftUIのリストの基本形
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
let areaName = ["東京", "大阪", "福岡", "沖縄"]
var body: some View {
List {
ForEach(areaName.indices, id: \.self) {
Text(areaName[$0])
}
}
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}
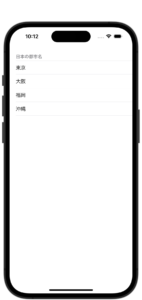
SwiftUIのリストにセクションを追加
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
let areaName = ["東京", "大阪", "福岡", "沖縄"]
var body: some View {
List {
Section(header: Text("日本の都市名")) {
ForEach(areaName.indices, id: \.self) {
Text(areaName[$0])
}
}
}
.listStyle(InsetListStyle())//セルと近いセクションデザイン。
//.listStyle モディファイア一覧。
//.listStyle(DefaultListStyle())//デフォルト
//.listStyle(InsetGroupedListStyle())//デフォルトに近いデザイン。
//.listStyle(PlainListStyle())//セルと近いセクションデザイン。
//.listStyle(InsetListStyle())//セルと近いセクションデザイン。
//.listStyle(GroupedListStyle())//設定画面に近いスタイル
//.listStyle(SidebarListStyle())//折りたたみデザイン。
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}
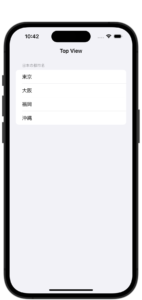
SwiftUIのリストにナビバーを追加
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
let areaName = ["東京", "大阪", "福岡", "沖縄"]
var body: some View {
NavigationStack {
List {
Section(header: Text("日本の都市名")) {
ForEach(areaName.indices, id: \.self) {
Text(areaName[$0])
}
}
}
.navigationTitle("Top View")
.navigationBarTitleDisplayMode(.inline)//表示スタイル
}
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}
SwiftUIでナビゲーションによる画面遷移
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
NavigationStack {
NavigationLink {
nextView()
} label: {
Text("NextViewへ")
}
}
}
}
struct nextView: View {
var body: some View {
Text("NextViewだよ。")
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}

SwiftUIのモーダルビュー
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
@State private var present = false
var body: some View {
Button("モーダルビュー") {
present = true
}
.sheet(isPresented: $present) {
ModalView()
}
}
}
struct ModalView: View {
@Environment(\.dismiss) private var dismiss
var body: some View {
Button("閉じる") {
dismiss()
}
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity, maxHeight: .infinity)
.background(Color.cyan.opacity(0.1))
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}
SwiftUIのモーダルフルスクリーン
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
@State var present = false
var body: some View {
Button("モーダルフルスクリーン"){
present = true
}
.fullScreenCover(isPresented: $present, onDismiss: didDismiss) {
ModalFullScreen(present2: $present)
}
}
func didDismiss() {
print("モーダルフルスクリーンが閉じたよ。")
}
}
struct ModalFullScreen: View {
@Binding var present2: Bool
var body: some View {
Button("閉じる") {
present2 = false
}
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity, maxHeight: .infinity)
.background(Color.cyan.opacity(0.1).edgesIgnoringSafeArea(.all))
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}
SwiftUIでナビバーを非表示にして、戻る。
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
NavigationView {
NavigationLink(destination: nextView()) {
Text("nextViewへ。")
}
}
}
}
struct nextView: View {
@Environment(\.presentationMode) var nextScreen
var body: some View {
Button("戻る"){
self.nextScreen.wrappedValue.dismiss()
}
.navigationBarHidden(true)
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}
NavigationStackとよる画面遷移
順番に画面遷移し、戻るで最初の画面に戻る。
import SwiftUI
var CountryArray:[String] = ["Japan", "America", "England"]
var CityTwoDimArray:[[String]] = [
["Tokyo", "Osaka", "Fukuoka"],
["Los Angeles", "New York", "Seattle"],
["London", "Cambridge", "Glasgow"]
]
struct FirstView: View {
@State var sectionNumber = 0
@State var goToSecondView = false
var body: some View {
NavigationStack {
List {
ForEach(CountryArray.indices, id: \.self) {section in
Button(CountryArray[section]) {
sectionNumber = section
goToSecondView = true
}
.foregroundColor(.primary)
}
.navigationDestination(isPresented: $goToSecondView) {
SecondView(sectionNumber: sectionNumber)
}
}
.navigationTitle("Country List")
}
}
}
struct SecondView:View{
var sectionNumber = 0
@State var rowNumber = 0
@State var goToThirdView = false
var body: some View {
NavigationStack{
List {
ForEach(CityTwoDimArray[sectionNumber].indices, id: \.self) {row in
Button(CityTwoDimArray[sectionNumber][row]) {
rowNumber = row
goToThirdView = true
}
.foregroundColor(.primary)
}
.navigationDestination(isPresented: $goToThirdView) {
ThirdView()
}
}
.navigationTitle("City List")
}
}
}
struct ThirdView:View{
@Environment(\.presentationMode) var thisScreen
var body: some View {
Button("戻る"){
self.thisScreen.wrappedValue.dismiss()
}
.foregroundColor(.primary)
}
}
#Preview {
FirstView()
}ButtonによるViewの入れ替え
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
@State var showViewName = "OrangeView"
var body: some View {
VStack {
Spacer()
//ここでviewの入れ替え。
VStack {
if showViewName == "OrangeView" {
OrangeView()
} else if showViewName == "CyanView" {
CyanView()
} else if showViewName == "PinkView" {
PinkView()
}
}
//.frame(maxWidth: .infinity, minHeight: UIScreen.main.bounds.height - 176)
Spacer()
//ここからボタン。
HStack (){
Spacer()
Button(action: {
showViewName = "OrangeView"
}) {
Image(systemName: "circle.fill")
}
.foregroundColor(.orange)
Spacer()
Button(action: {
showViewName = "CyanView"
}) {
Image(systemName: "circle.fill")
}
.foregroundColor(.cyan)
Spacer()
Button(action: {
showViewName = "PinkView"
}) {
Image(systemName: "circle.fill")
}
.foregroundColor(.pink)
Spacer()
}
.font(.system(size: 25))
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity, minHeight: 54.0)
.background(Color.gray.opacity(0.2)) // OK
}
.onChange(of: showViewName) {
print(showViewName)
}
}
}
struct OrangeView: View {
var body: some View {
Text("OrangeView")
.foregroundColor(.orange)
.font(.system(size:35))
.fontWeight(.black)
}
}
struct CyanView: View {
var body: some View {
Text("CyanView")
.foregroundColor(.cyan)
.font(.system(size:35))
.fontWeight(.black)
}
}
struct PinkView: View {
var body: some View {
Text("PinkView")
.foregroundColor(.pink)
.font(.system(size:35))
.fontWeight(.black)
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}
SwiftUIのCharts(iOS16〜)
import SwiftUI
import Charts
struct ContentView: View {
//表の基礎のなるリスト。
@State var priceList:[[Any]] = [
["りんご", 200, Color(#colorLiteral(red: 1, green: 0.1857388616, blue: 0.5733950138, alpha: 1))],
["なし", 300, Color(#colorLiteral(red: 1, green: 0.4932718873, blue: 0.4739984274, alpha: 1))],
["みかん", 300, Color(#colorLiteral(red: 1, green: 0.8323456645, blue: 0.4732058644, alpha: 1))],
["スイカ", 1800, Color(#colorLiteral(red: 0.9995340705, green: 0.988355577, blue: 0.4726552367, alpha: 1))],
["ぶどう", 800, Color(#colorLiteral(red: 0.8321695924, green: 0.985483706, blue: 0.4733308554, alpha: 1))],
["シャインマスカット", 1500, Color(#colorLiteral(red: 0.4500938654, green: 0.9813225865, blue: 0.4743030667, alpha: 1))],
["クランベリー", 800, Color(#colorLiteral(red: 0.4508578777, green: 0.9882974029, blue: 0.8376303315, alpha: 1))],
]
var body: some View {
Chart {
ForEach(priceList.indices, id: \.self) { num in
BarMark(
x: .value("fruit", priceList[num][0] as! String),
y: .value("Price", priceList[num][1] as! Int)
)
.foregroundStyle(by: .value("Shape Color", priceList[num][0] as! String))
}
}
.chartForegroundStyleScale(range: graphColors(priceList:priceList))
.padding()
HStack (){
Spacer()
Button(action: {
PulusButtonAction()
}) {
Image(systemName: "plus.circle")
}
.foregroundColor(.orange)
Spacer()
Button(action: {
MinusButtonAction()
}) {
Image(systemName: "minus.circle")
}
.foregroundColor(.cyan)
Spacer()
}
.font(.system(size: 25))
}
//色の配列を返すファンクション。
func graphColors(priceList:[[Any]]) -> [Color] {
var returnColors:[Color] = []
for number in priceList.indices {
returnColors.append(priceList[number][2] as! Color)
}
return returnColors
}
//プラスボタンのアクション。
func PulusButtonAction(){
print("プラスボタンだよ。")
priceList.append(["メロン", 1800, Color(#colorLiteral(red: 0.476841867, green: 0.5048075914, blue: 1, alpha: 1))])
}
//マイナスボタンのアクション。
func MinusButtonAction(){
print("マイナスボタンだよ。")
if priceList.count != 0 {
priceList.removeLast()
}
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}BarMark
xとyを入れ替えると、横向きになる。
PointMark
RectangleMark
LineMark
.foregroundStyleの行を
.foregroundStyle(.red)に変更する。
SwiftUIのChartsのBarMarkの積層(iOS16〜)
import SwiftUI
import Charts
struct ContentView: View {
struct kamoku: Identifiable {
var id = UUID()
let kamoku: String
let color: Color
}
@State var kamokuList: [kamoku] = [
kamoku(id: UUID(), kamoku : "国語", color:Color(#colorLiteral(red: 1, green: 0.1857388616, blue: 0.5733950138, alpha: 1))),
kamoku(id: UUID(), kamoku : "算数", color:Color(#colorLiteral(red: 0.9995340705, green: 0.988355577, blue: 0.4726552367, alpha: 1))),
kamoku(id: UUID(), kamoku : "理科", color:Color(#colorLiteral(red: 0.2392156869, green: 0.6745098233, blue: 0.9686274529, alpha: 1))),
kamoku(id: UUID(), kamoku : "社会", color:Color(#colorLiteral(red: 0.4508578777, green: 0.9882974029, blue: 0.8376303315, alpha: 1))),
]
//表の基礎のなるリスト。
@State var studyList:[[Any]] = [
["2023年1月1日", 200,"国語"],
["2023年1月1日", 200, "算数"],
["2023年1月2日", 300, "理科"],
["2023年1月3日", 300, "社会"],
["2023年1月3日", 1800, "国語"],
["2023年1月3日", 800, "算数"],
["2023年1月4日", 1500, "理科"],
["2023年1月5日", 800, "社会"],
]
var body: some View {
Chart {
ForEach(studyList.indices, id: \.self) { num in
BarMark(
x: .value("日時", studyList[num][0] as! String),
y: .value("時間", studyList[num][1] as! Int)
)
.foregroundStyle(by: .value("Shape Color", studyList[num][2] as! String))
}
}
.chartForegroundStyleScale(
domain: kamokuList.map{ $0.kamoku }, range: kamokuList.map{ $0.color }
)
.padding()
HStack (){
Spacer()
Button(action: {
PulusButtonAction()
}) {
Image(systemName: "plus.circle")
}
.foregroundColor(.orange)
.font(.system(size: 35))
Spacer()
Button(action: {
SmallPulusButtonAction()
}) {
Image(systemName: "plus")
}
.foregroundColor(.orange)
.font(.system(size: 25))
Spacer()
}
.font(.system(size: 25))
}
//プラスボタンのアクション。
func PulusButtonAction(){
print("プラスボタンだよ。")
studyList.append(["2023年1月6日", 1200, "国語"])
}
//マイナスボタンのアクション。
func SmallPulusButtonAction(){
print("スモールプラスボタンだよ。")
kamokuList.append(kamoku(id: UUID(), kamoku : "英語", color:.red))
}
}
//
#Preview {
ContentView()
}SwiftUIのChartsのBarMarkの並列(iOS16〜)
import SwiftUI
import Charts
struct ContentView: View {
struct kamoku {
var kamoku: String
var color: Color
}
@State var kamokuList: [kamoku] = [
kamoku(kamoku : "国語", color:Color(#colorLiteral(red: 1, green: 0.1857388616, blue: 0.5733950138, alpha: 1))),
kamoku(kamoku : "数学", color:Color(#colorLiteral(red: 1, green: 0.8323456645, blue: 0.4732058644, alpha: 1))),
kamoku(kamoku : "社会", color:Color(#colorLiteral(red: 0.8321695924, green: 0.985483706, blue: 0.4733308554, alpha: 1))),
]
struct StudyRecord: Identifiable {
var id = UUID()
var date: String
var kamoku: String
var time: Int
}
@State var StudyList:[StudyRecord] = [
StudyRecord(id: UUID(), date : "2023年1月4日", kamoku : "国語", time : 800),
StudyRecord(id: UUID(), date : "2023年1月4日", kamoku : "数学", time : 1000),
StudyRecord(id: UUID(), date : "2023年1月4日", kamoku : "社会", time : 1200),
StudyRecord(id: UUID(), date : "2023年1月5日", kamoku : "国語", time : 1800),
StudyRecord(id: UUID(), date : "2023年1月5日", kamoku : "数学", time : 1200),
StudyRecord(id: UUID(), date : "2023年1月5日", kamoku : "社会", time : 700),
StudyRecord(id: UUID(), date : "2023年1月6日", kamoku : "国語", time : 1200),
StudyRecord(id: UUID(), date : "2023年1月6日", kamoku : "数学", time : 3000),
StudyRecord(id: UUID(), date : "2023年1月6日", kamoku : "社会", time : 3300),
]
var body: some View {
Chart {
ForEach(StudyList) { StudyList in
BarMark(
x: .value("日時", StudyList.date),
y: .value("時間", StudyList.time)
)
.foregroundStyle(by: .value("kamoku", StudyList.kamoku))
.position(by: .value("kamoku", StudyList.kamoku))
}
}
.chartForegroundStyleScale(domain: kamokuList.map{ $0.kamoku }, range: kamokuList.map{ $0.color })
.padding()
HStack (){
Spacer()
Button(action: {
PulusButtonAction()
}) {
Image(systemName: "plus.circle")
}
.foregroundColor(.orange)
.font(.system(size: 35))
Spacer()
Button(action: {
SmallPulusButtonAction()
}) {
Image(systemName: "plus")
}
.foregroundColor(.orange)
.font(.system(size: 25))
Spacer()
}
.font(.system(size: 25))
}
//プラスボタンのアクション。
func PulusButtonAction(){
print("プラスボタンだよ。")
StudyList.append(StudyRecord(id: UUID(), date : "2023年1月7日", kamoku : "国語", time : 1200))
StudyList.append(StudyRecord(id: UUID(), date : "2023年1月7日", kamoku : "数学", time : 800))
StudyList.append(StudyRecord(id: UUID(), date : "2023年1月7日", kamoku : "社会", time : 1000))
//StudyList.append(StudyRecord(id: UUID(), date : "2023年1月7日", kamoku : "理科", time : 1000))
}
//マイナスボタンのアクション。
func SmallPulusButtonAction(){
print("スモールプラスボタンだよ。")
kamokuList.append(kamoku(kamoku : "理科",color:.red))
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}SwiftUIのテキストフィールド付きのAlert
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
@State var textFieldString = ""
@State var showAlert: Bool = false
var body: some View {
Button("alert") {
textFieldString = ""
showAlert = true
}
.alert("Alert", isPresented: $showAlert) {
TextField("Passcode", text: $textFieldString)
Button("OK") {
showAlert = false
print("OK \(textFieldString)\(showAlert)")
}
Button("Cancel", role: .cancel){
showAlert = false
print("Cancel \(textFieldString)\(showAlert)")
}
}
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}SwiftUIのPickerの横向き
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
@State var Imageviews = [
Image(systemName: "bicycle"),
Image(systemName: "car"),
Image(systemName: "bus"),
Image(systemName: "lightrail"),
Image(systemName: "airplane"),
]
@State private var indexNumber = 0
var body: some View {
VStack {
Picker(selection: $indexNumber, label: Text("")) {
ForEach(Imageviews.indices, id: \.self) { indexNumber in
Imageviews[indexNumber]
}
}
.pickerStyle(SegmentedPickerStyle())
}
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}UIKit内でSwiftUIを表示する
import UIKit
import SwiftUI
class SecondViewController: UIViewController {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
let vc: UIHostingController = UIHostingController(rootView: SubView())
self.addChild(vc)
self.view.addSubview(vc.view)
vc.didMove(toParent: self)
vc.view.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
//vc.view.heightAnchor.constraint(equalToConstant: 320).isActive = true
vc.view.bottomAnchor.constraint(equalTo: self.view.bottomAnchor, constant: 0).isActive = true
vc.view.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: self.view.topAnchor, constant: 0).isActive = true
vc.view.leftAnchor.constraint(equalTo: self.view.leftAnchor, constant: 0).isActive = true
vc.view.rightAnchor.constraint(equalTo: self.view.rightAnchor, constant: 0).isActive = true
//vc.view.centerYAnchor.constraint(equalTo: self.view.centerYAnchor).isActive = true
}
struct SubView : View {
var body: some View {
List {
ForEach(0...15, id: \.self) {
Text("\($0)")
}
}
}
}
}SwiftUIでの図形表示
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
List() {
//四角
Rectangle()
.fill(.orange)
.frame(width:300, height: 100)
//グラデーション
let gradient = LinearGradient(gradient: Gradient(colors: [.pink, .orange]), startPoint: .topLeading, endPoint: .bottomTrailing)
Rectangle()
.fill(gradient)
.frame(width:300, height: 100)
//角丸
RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 30)
.fill(.pink)
.frame(width:300, height: 100)
.overlay(Text("momo")
.foregroundColor(.white))
.font(.title)
//角丸の変形
RoundedRectangle(cornerSize: .init(width: 100, height: 20))
.fill(Color.red)
.frame(width:300, height: 100)
//カプセル
Capsule()
.fill(gradient)
.frame(width:300, height: 100)
//丸
Circle()
.fill(Color.orange)
.frame(width:100, height: 100)
//楕円
Ellipse()
.fill(Color.pink)
.frame(width:200, height: 100)
}
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}SwiftUIでつまんで動かす
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
@State var center = CGPoint.zero
var body: some View {
VStack {
Text("🍎")
.font(.system(size: 50))
.frame(width: 50, height: 50)
.offset(x: center.x - 25, y: center.y - 25)
.gesture(
DragGesture(minimumDistance: 0).onChanged { value in
center = value.location
})
}
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}SwiftUIでの時間付きアニメーション
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
@State var kurukuru = true
var body: some View {
VStack {
Text("🍙")
.font(.system(size: 100))
.rotationEffect(Angle.degrees(kurukuru ? 0 : 720))
.animation(Animation.easeInOut(duration:3.0), value: kurukuru)
.padding()
Button(action: {
kurukuru.toggle()
}) {
Image(systemName: "arrow.clockwise")
.font(.system(size: 50))
.foregroundColor(.secondary)
}
.padding()
}
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}SwiftUIのToggleによるアニメーション
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
@State var sizeChangeOn = false
var body: some View {
VStack {
Spacer()
Circle()
.fill(sizeChangeOn ? .orange.opacity(0.5) : .orange)
.frame(width: 200, height: 200)
.scaleEffect(sizeChangeOn ? 0.5 : 1.0)
Spacer()
Circle()
.fill(sizeChangeOn ? .cyan : .cyan.opacity(0.5))
.frame(width: 200, height: 200)
.scaleEffect(sizeChangeOn ? 1.0 : 0.5)
Spacer()
Toggle("", isOn: $sizeChangeOn.animation(Animation.easeInOut(duration:2.0)))
.labelsHidden()
.tint(.orange)
Spacer()
}
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}SwiftUIのボタンのアニメーション
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
@State private var treeOn: Bool = false
var body: some View {
Button {
treeOn.toggle()
} label: {
VStack{
Spacer()
Text("🌲")
.font(.system(size: 50))
.frame(width: 50, height: 50)
.scaleEffect(treeOn ? 6 : 1)
.animation(Animation.easeInOut(duration:3.0), value: treeOn)
Spacer()
}
}
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}SwiftUIにおけるボタンエフェクト
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
Button(action: {
}) {
Text("Tap Me !")
}.buttonStyle(BigButton())
}
}
struct BigButton: ButtonStyle {
func makeBody(configuration: Configuration) -> some View {
configuration.label
.padding()
.background(configuration.isPressed ? .pink : .orange)
.foregroundStyle(.white)
.clipShape(Capsule())
.scaleEffect(configuration.isPressed ? 4.0 : 1)
.animation(.easeOut(duration: 2.0), value: configuration.isPressed)
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}SwiftUIの.timingCurve
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
@State private var animate = false
var body: some View {
ZStack {
Circle()
.frame(width: 220, height: 220)
.foregroundColor(.gray.opacity(0.3))
Circle()
.frame(width: 160, height: 160)
.foregroundColor(.white)
Circle()
.frame(width: 30, height: 30)
.foregroundColor(Color.orange)
.offset(y: 95)
.rotationEffect(.degrees(self.animate ? 540 : 180))
.animation(
Animation//頂点から0.9がスタート。
.timingCurve(0.9, 0.2, 0.1, 0.8, duration: 3.3)
.repeatForever(autoreverses: false), value: animate
)
Circle()
.frame(width: 20, height: 20)
.foregroundColor(Color.pink)
.offset(y: 90)
.rotationEffect(.degrees(self.animate ? 540 : 180))
.animation(
Animation//頂点から0.9がスタート。
.timingCurve(0.9, 0.2, 0.1, 0.8, duration: 4.0)
.repeatForever(autoreverses: false), value: animate
)
}
.onAppear() {
self.animate = true
}
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}SwiftUIのアニメーションの演習
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
@State var animationOn = false
var body: some View {
ZStack {
ForEach (1...500, id:\.self) { _ in
Circle ()
.foregroundColor(Color (red: .random(in: 0.0...0.4),
green: .random(in: 0.8...1.0),
blue: .random(in: 0.3...0.7)))
.opacity(.random(in: 0.1...0.2))
.animation (Animation.spring (dampingFraction: 0.5)
.repeatForever()
.speed (.random(in: 0.05...0.4))
.delay(.random (in: 0...1)), value: animationOn
)
.scaleEffect(.random(in: 0.1...2))
.frame(width: .random(in: 15...40),
height: CGFloat.random (in: 15...40),
alignment: .center)
.position(CGPoint(x: .random(in: 0...400),
y: .random (in: 0...834)))
}
}
.opacity(animationOn ? 0.0 : 1.0)
.animation(Animation.easeInOut(duration:3.0),value: animationOn)
.background(.white)
.onTapGesture {
animationOn.toggle()
}
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
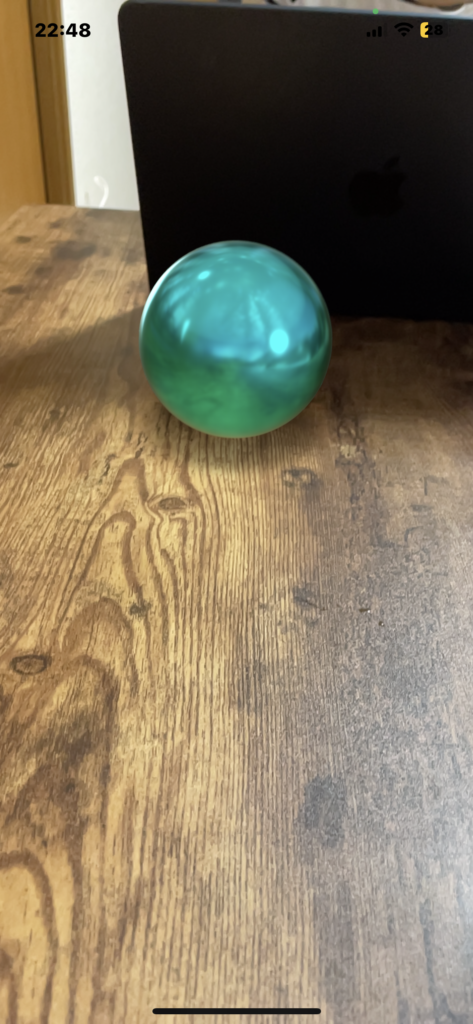
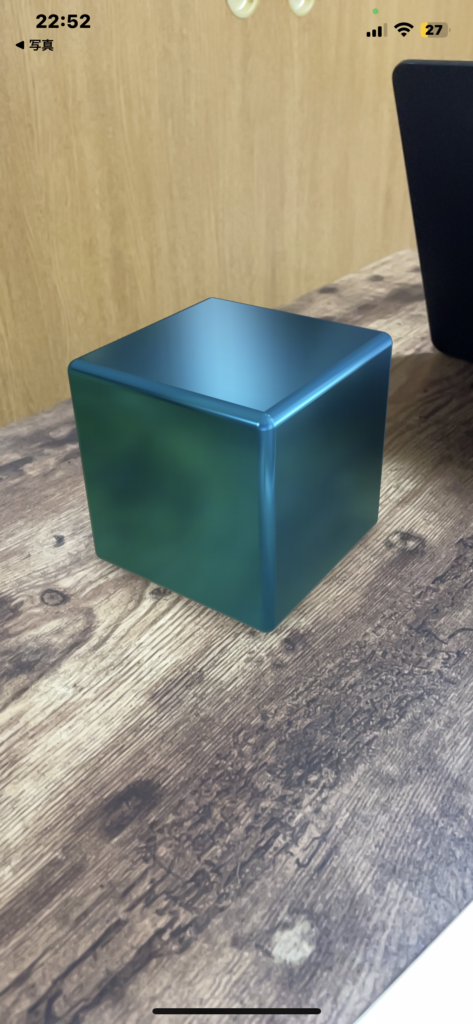
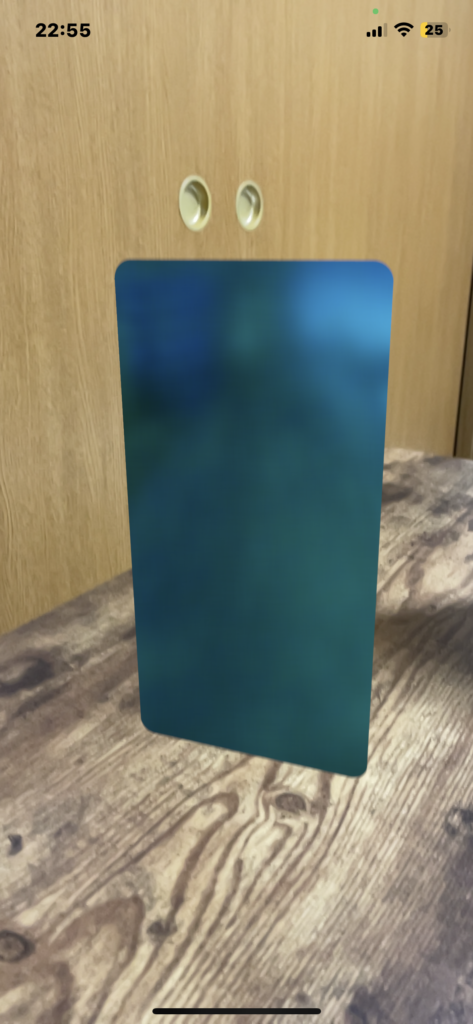
}RealityKitとSwiftUIで、球体とボックスと平面を表示する。
import SwiftUI
import RealityKit
struct ContentView : View {
var body: some View {
RealityKitSampleNo1().edgesIgnoringSafeArea(.all)
}
}
struct RealityKitSampleNo1: UIViewRepresentable {
func makeUIView(context: Context) -> ARView {
let arView = ARView(frame: .zero)
let mesh = MeshResource.generateSphere(radius: 0.051)//球体。
//let mesh = MeshResource.generateBox(size: 0.1, cornerRadius: 0.005)//box
//let mesh = MeshResource.generatePlane(width: 0.15, height: 0.30, cornerRadius: 0.010)//平面。
let material = SimpleMaterial(color: .cyan, roughness: 0.15, isMetallic: true)
let model = ModelEntity(mesh: mesh, materials: [material])
model.transform.translation.y = 0.05
let anchor = AnchorEntity(.plane(.horizontal, classification: .any, minimumBounds: SIMD2<Float>(0.2, 0.2)))
anchor.children.append(model)
arView.scene.anchors.append(anchor)
return arView
}
func updateUIView(_ uiView: ARView, context: Context) {
}
}


RealityKitとSwiftUIで、文字オブジェクトを表示する。
import SwiftUI
import RealityKit
struct ContentView : View {
var body: some View {
RealityKitSampleNo1().edgesIgnoringSafeArea(.all)
}
}
struct RealityKitSampleNo1: UIViewRepresentable {
func makeUIView(context: Context) -> ARView {
let arView = ARView(frame: .zero)
let textMesh = MeshResource.generateText("Hello, world!", extrusionDepth: 0.1, font: .systemFont(ofSize: 0.5), containerFrame: CGRect.zero, alignment: .left, lineBreakMode: .byTruncatingTail)
let textMaterial = SimpleMaterial(color: .systemCyan, roughness: 0.0, isMetallic: true)
let textModel = ModelEntity(mesh: textMesh, materials: [textMaterial])
textModel.scale = SIMD3<Float>(0.1, 0.1, 0.1)
textModel.position = SIMD3<Float>(0.0, 0.0, -0.2)
let anchor = AnchorEntity(.plane(.horizontal, classification: .any, minimumBounds: SIMD2<Float>(0.2, 0.2)))
anchor.children.append(textModel)
arView.scene.anchors.append(anchor)
return arView
}
func updateUIView(_ uiView: ARView, context: Context) {}
}

RealityKitとSwiftUIで、usdzファイルを表示する。端末基準。
import SwiftUI
import RealityKit
struct ContentView : View {
var body: some View {
RealityKitSampleNo1().edgesIgnoringSafeArea(.all)
}
}
struct RealityKitSampleNo1: UIViewRepresentable {
func makeUIView(context: Context) -> ARView {
let arView = ARView(frame: .zero)
let filename = "toy_drummer_idle"
let modelUrl = Bundle.main.url(forResource: filename, withExtension: "usdz")!
let anchor = AnchorEntity(world: [0, -0.2, -0.2])//自分から見て前方下に配置。
arView.scene.addAnchor(anchor)
if let modelEntity = try? ModelEntity.load(contentsOf: modelUrl) {
modelEntity.scale = SIMD3<Float>(0.01, 0.01, 0.01)
modelEntity.availableAnimations.forEach {
modelEntity.playAnimation($0.repeat())
}
anchor.addChild(modelEntity)
}
return arView
}
func updateUIView(_ uiView: ARView, context: Context) {}
}
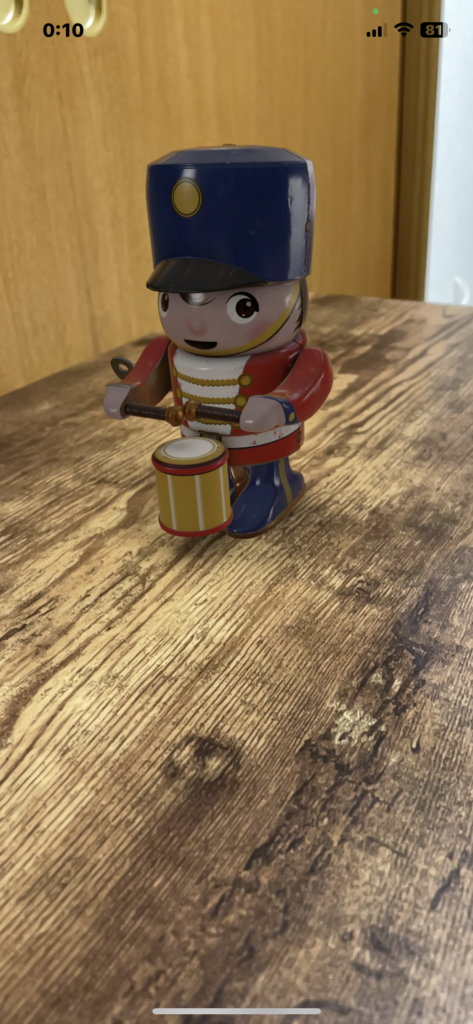
RealityKitとSwiftUIで、usdzファイルを表示する。平面基準。
import SwiftUI
import RealityKit
struct ContentView : View {
var body: some View {
RealityKitSampleNo1().edgesIgnoringSafeArea(.all)
}
}
struct RealityKitSampleNo1: UIViewRepresentable {
func makeUIView(context: Context) -> ARView {
let arView = ARView(frame: .zero)
let filename = "toy_drummer_idle"
let modelUrl = Bundle.main.url(forResource: filename, withExtension: "usdz")!
let anchor = AnchorEntity(.plane(.horizontal, classification: .any, minimumBounds: SIMD2<Float>(0.2, 0.2)))
//平面を取得して、平面を基準にオブジェクトを配置。
if let modelEntity = try? ModelEntity.load(contentsOf: modelUrl) {
modelEntity.scale = SIMD3<Float>(0.01, 0.01, 0.01)
modelEntity.availableAnimations.forEach {
modelEntity.playAnimation($0.repeat())
}
anchor.addChild(modelEntity)
}
arView.scene.addAnchor(anchor)
return arView
}
func updateUIView(_ uiView: ARView, context: Context) {}
}
RealityKitとSwiftUIで、3つのusdzファイルを表示する。平面基準。
Appleの3Dオブジェクトのサンプル
Quick Look Gallery - Augmented Reality - Apple Developer
Embed Quick Look views in your apps and websites to let users see incredible detailed renderings in 3D or AR.
import SwiftUI
import RealityKit
struct ContentView : View {
var body: some View {
RealityKitSampleNo1().edgesIgnoringSafeArea(.all)
}
}
struct RealityKitSampleNo1: UIViewRepresentable {
func makeUIView(context: Context) -> ARView {
let arView = ARView(frame: .zero)
let filename = "toy_drummer_idle"
let modelUrl = Bundle.main.url(forResource: filename, withExtension: "usdz")!
let anchor = AnchorEntity(.plane(.horizontal, classification: .any, minimumBounds: SIMD2<Float>(0.2, 0.2)))
if let modelEntity = try? ModelEntity.load(contentsOf: modelUrl) {
modelEntity.scale = SIMD3<Float>(0.01, 0.01, 0.01)
modelEntity.availableAnimations.forEach {
modelEntity.playAnimation($0.repeat())
}
//modelEntity.position = [0, -0.15, 0]
anchor.addChild(modelEntity)
}
let filename2 = "Earth_1_12756"
let modelUrl2 = Bundle.main.url(forResource: filename2, withExtension: "usdz")!
if let modelEntity = try? ModelEntity.load(contentsOf: modelUrl2) {
modelEntity.scale = SIMD3<Float>(0.0005, 0.0005, 0.0005)
modelEntity.availableAnimations.forEach {
modelEntity.playAnimation($0.repeat())
}
modelEntity.position = [0.2, 0.3, 0]
anchor.addChild(modelEntity)
}
let filename3 = "toy_biplane_idle"
let modelUrl3 = Bundle.main.url(forResource: filename3, withExtension: "usdz")!
if let modelEntity = try? ModelEntity.load(contentsOf: modelUrl3) {
modelEntity.scale = SIMD3<Float>(0.01, 0.01, 0.01)
modelEntity.availableAnimations.forEach {
modelEntity.playAnimation($0.repeat())
}
modelEntity.position = [-0.2, 0.1, 0]
anchor.addChild(modelEntity)
}
arView.scene.addAnchor(anchor)
return arView
}
func updateUIView(_ uiView: ARView, context: Context) {}
}


